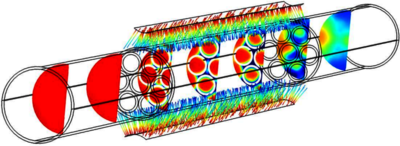
CFD Investigation of a Photocatalytic Multi-Tube Reactor for Indoor Air Purification
In industrial countries, people spend most of their time indoors. Stringent heat-insulation measures in combination with deficient ventilation have a negative impact on indoor air quality [1]. Integration or retrofitting of a photocatalytic oxidation or PCO reactor into continuous flow systems like HVAC (Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning) equipment is an interesting approach for abating indoor air pollution [2]. The PCO purification method exposes a catalyst like titanium dioxide (TiO2), to ultraviolet (UV) light to produce hydroxyl radicals and superoxide anions. These radicals are extremely reactive and are able to oxidize harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into H20 and CO2. PCO technology is very cost-effective, efficient and it does not produce any waste streams. An in-depth CFD investigation of a novel parallel flow tube reactor was made. Determining the kinetic parameters, describing the PCO reactions, is an important step in the development of efficient air purification units for integration in HVAC systems. In this work, we estimated the 'intrinsic' PCO related light-dependent (ray-optics) kinetic parameters (adsorption, desorption and photocatalytic rate constants as well as the total number of active sites), by comparing results from a multiphysics model including kinetic rate expressions with experimental results using an optimization approach (Optimization Module). Acetaldehyde was chosen as a model VOC (Transport of Diluted Species interface coupled to the Laminar Flow interface). Contrary to analytical methods, which often oversimplify the physical and chemical phenomena, CFD and multiphysics can take into account the geometric design of the reactor and all relevant characteristics of the air flow [3].
[1] B. Kartheuser, N. Costarramone, T. Pigot, and S. Lacombe, “NORMACAT project: normalized closed chamber tests for evaluation of photocatalytic VOC treatment in indoor air and formaldehyde determination.,” Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int., vol. 19, no. 9, pp. 3763–71, 2012. [2] J. Zhao and X. Yang, “Photocatalytic oxidation for indoor air purification: a literature review,” Build. Environ., vol. 38, no. 5, pp. 645–654, 2003. [3] J. van Walsem, S.W. Verbruggen, B. Modde, S. Lenaerts, S. Denys, CFD investigation of a multi-tube photocatalytic reactor in non-steady- state conditions, Chem. Eng. J. 304 (2016) 808–816.
下载
- van walsem_poster.pdf - 0.27MB
- van walsem_abstract.pdf - 0.02MB
