Simulation Study of Electron Beam Profile Near the Aperture of Hollow Cathode for High Current Density Electron Beam Generation using COMSOL Multiphysics®
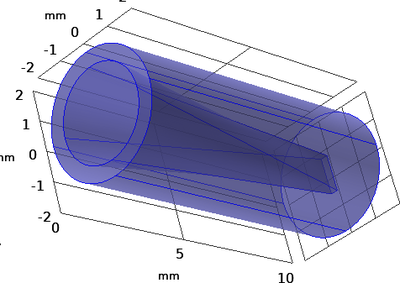
High power Terahertz (THz) sources have become a topic of great interest for a wide variety of applications from medical science to security systems and from material science to telecommunication. The high output power of these THz sources mainly depends upon high current density and energetic electron beams [1, 2]. The current density of electron beam primarily depends upon the shape of the electron beam. Therefore, a comparative simulation study has been performed using COMSOL Multiphysics® to see the effect of different shapes of electron beam on the current density of the beam. The simulation study has been performed using Particle Tracing module. A three dimensional geometry has been constructed which consists of a beam emitter front and acts as cathode. Beam emitter has a diameter of 3mm which is equal to the size of the aperture of cathode. This is followed by a down tapering into different shapes like circular, sheet and elliptical. The other end of this tapered adapter region, area of the different shapes of aperture has been kept constant and is equal to 1.25mm by 0.25mm i.e., 0.3125mm square and it acts as a beam collector.
For all the three shapes, the current density of the beam at the collector end has been compared and the beam profile has been studied. It has been observed that the sheet aperture is found to have the highest current density followed by the elliptical aperture and the cylindrical aperture has the lowest current density. The study has been performed for accelerating voltage range of 20-40 kV with a step size of 5kV. An analysis has also been performed to see the effect of the length of the tapered region on the current density of the beam at the collector end. Poincare maps have been used to analyse the beam profile at different distances inside the adapter region and near the collector region.
下载
- COMSOL_Bangalore_2019_NikitaGurjar.pdf - 0.73MB
- COMSOL Conf ppt.pdf - 0.76MB
