Thermal Battery Simulation Models: Evaluating Levels of Abstraction and Geometric Resolution
The accurate modeling and simulation of battery cells are crucial for the optimization and design of efficient energy storage systems. The choice of an appropriate battery simulation model heavily depends on the specific problem being investigated. This poster presents a comparative analysis of battery simulation models with varying levels of abstraction and geometric resolution, employing the COMSOL Multiphysics® software. Specifically, the Heat Transfer Module and Equivalent Electrical Circuit (ECM) modeling within COMSOL® are utilized for the simulation and analysis of battery behavior.
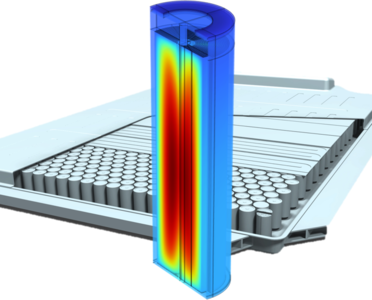
Battery simulation models with different levels of abstraction provide varying degrees of detail and computational efficiency. In this study we compare different 3D battery cylindrical cell models which differ significantly in the geometric representation and especially in the Jelly Roll. Each model is implemented and simulated using COMSOL Multiphysics®, and their respective advantages and limitations are explored. The most detailed 3D model represents the battery with high fidelity, capturing high resolution geometrical features and thermal distributions, which is also useful for tab-design.
However, this level of detail comes at the cost of increased computational resources and simulation time. The most simplified geometry comes with the shortest calculation time. At the same time, however, accuracy differs. The goal is to find a simplified 3D geometric model that strikes a balance between accuracy and computational efficiency, allowing for faster simulations while still capturing important thermal battery effects. To evaluate and compare these models, key performance metrics such as temperature distribution, current distribution, and cell voltage are analyzed and compared across the different simulation approaches.
The results from this work highlight the importance of selecting an appropriate battery simulation model based on the specific problem and available computational resources. Overall, this study provides valuable insights into the selection and application of battery simulation models, which enables researchers and engineers to develop efficient and optimized energy storage systems.
下载
- Schoß_6481_poster.pdf - 3.31MB
